The changing meaning of product and design engineering
The term "product" can evoke a wide range of images in mind. When you walk into a retail store, you pick up products—things that satisfy your needs and want. It can be shampoo, a pair of shoes, a kitchen appliance, or any tangible, portable, and feelable object. The product they choose should add value to their lives, and design engineers create it that way to provide consumers with what they desire — utility. That's how consumers are conditioned to behave.
If you’re looking for expert support in creating valuable, well-designed products, explore our product design services in NZ to see how we can help bring your idea to life.
However, as digitisation started shaping societies and people's mental perceptions, the definition of a product has extended far beyond its economic connotation to include consumers' overall experience. With the increasing use of smartphones and hand-held devices, all websites, mobile applications, and other digital applications are considered products capable of crafting equally memorable and practical experiences as their physical counterparts. As product design has taken a whole new shape with the advent of digital technologies, it's time that the job description of design engineers also levels up to the evolution. Without implementing innovative solutions, a product engineer would not be able to deliver a successful new product — be it physical or digital. Long-lasting transformation takes place when there's a shift in perspective, and this purpose can only be achieved when a design engineer has a crystal-clear understanding of what they are supposed to do.
As product design has taken a whole new shape with the advent of digital technologies, it's time that the job description of design engineers also levels up to the evolution. Without implementing innovative solutions, a product engineer would not be able to deliver a successful new product — be it physical or digital. Long-lasting transformation takes place when there's a shift in perspective, and this purpose can only be achieved when a design engineer has a crystal-clear understanding of what they are supposed to do.
Typically, a design engineer is expected to translate ideas into tangible, real products. Mechanical engineers are supposed to work out the mechanics of a product, such as a piece of factory equipment or machine. But a career in design engineering can be slightly more challenging than mechanical engineering. Design engineering has a much broader scope because it requires the perfect blend of creativity, project management, and engineering.
Design engineers perform in-depth research and come up with ideas for new products. They can also alter existing products or change manufacturing processes to boost efficiency or performance. Typically, they work on almost every consumer product imaginable for large-scale production of any daily-use item—from smartphones to automobiles to kitchen appliances to medical equipment.
What is product design?
Now that you know what a product engineer does, let’s talk about what product design is. In essence, product design entails all the processes to identify a market opportunity and the problem, create innovative solutions, and offer them to people. Each user has an issue to deal with, and effective product design is all about touching these pain points with a relevant solution. That’s why time and again, it has been emphasized that new products that a design engineer creates should create real value for users. Such innovative solutions come from an imaginative mind—someone who knows and understands the user in and out.

There are three basic components in product design:
- Appearance
- Functionality
- Performance quality
A design engineer who keeps these three components together with a creative and innovative approach can definitely create a great product. Such a professional often creates competitive products that are known for their modern, attractive appearance, value-adding convenience, and high-performing functionality.
The importance of design thinking in product design
 The creation of new products that set marks successfully in the world occurs due to design thinking employed by design engineers. If you aren’t aware of what design thinking is, then it’s a non-linear process or approach to product design. Design thinking aims to understand the end-users of new products and identify their problems by delving deeper beneath the surface.
The creation of new products that set marks successfully in the world occurs due to design thinking employed by design engineers. If you aren’t aware of what design thinking is, then it’s a non-linear process or approach to product design. Design thinking aims to understand the end-users of new products and identify their problems by delving deeper beneath the surface.
Over the years, design thinking has gained tremendous popularity among business owners and product designers. Such a way of thinking challenges existing product notions, giving design engineers a deeper view of who their end users are and why they want a product. Creating trendy or cool new products is excellent, but product design must keep the utility factor in mind so that the outcome is usable, functional, and successful.
Steps involved in product design
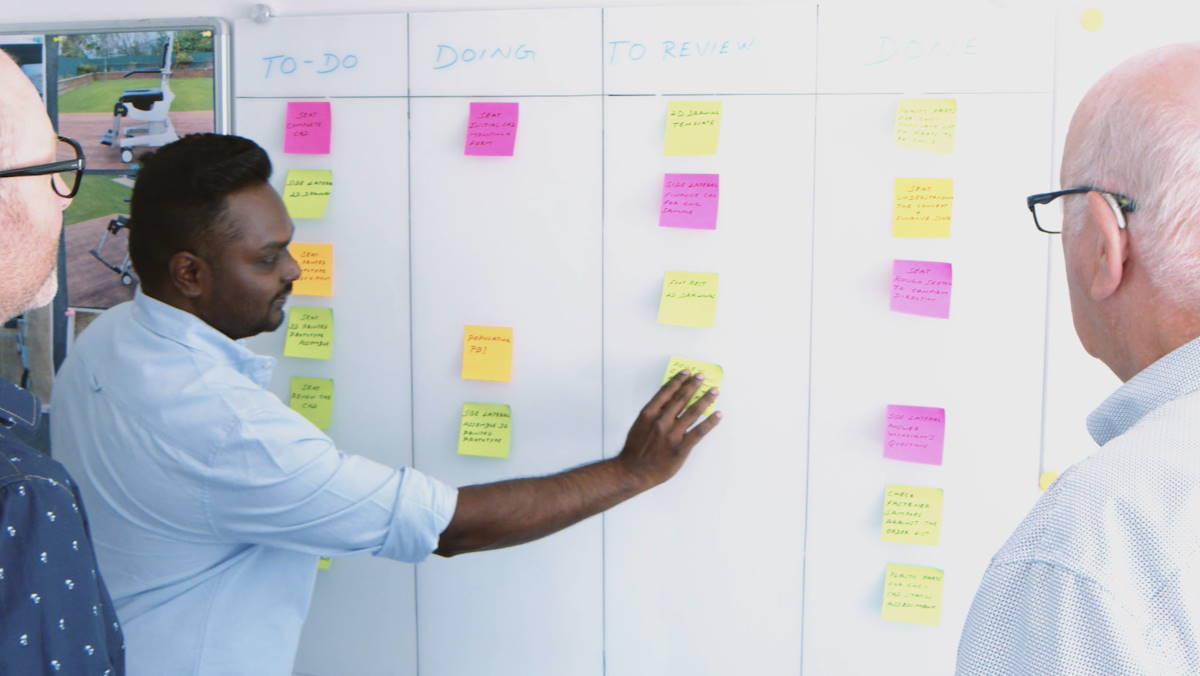
So far, we have discussed what product design is and how digitization has changed it. Now, let’s talk a little about the technical aspects. Generally, product design is divided into the following five phases:

1. Brainstorm ideas to launch new products within the team.
2. Identify consumers' desires (pain points) and the solutions that can fulfil them.
3. Documenting technical specifications or product requirements.
4. Dividing the implementation process into various iterations
5. Evaluating, testing, and modifying new products
A design engineer must have a crystal-clear idea of these five phases as a part of their job description. But consulting engineers or designers should look further at the following steps to implement the five phases properly.
1. Brainstorming ideas

Brainstorming is the first step in product design. It takes place in three phases:
Problem statement: Defining the target audience's problem sets the ground for all other phases and steps to follow. This part of the brainstorming session lays down the reason to create the right product design.
Ideation: Design engineers then take a creative approach to generate as many ideas as possible. Even the most absurd ideas are laid down because they can be a source of inspiration.
Idea selection: After generating ideas, it’s time to winnow the best ones. The most viable ideas are selected so that they are in line with the problem statement.
2. User research
A successful product design keeps the end-users in mind. Moreover, it’s incredibly crucial to develop a clear understanding of the market so that consulting engineers or designers can come up with a relevant creation. It’s imperative to collect data related to users, such as age, gender, income, marital status, geography, employment status, and psychological makeup. Ideally, business analysts and marketers usually perform this task as a part of their job description. However, such data is essential even for design engineers because it gives them an idea of the end users’ persona. Creating a user-focused product design becomes more manageable when a design engineer is armed with this data.
3. Creating conceptual design

After brainstorming and user research comes product concept development and refinement. In this step, a design engineer translates the problem statement (defined in step 1) into various conceptual designs. Depending on the complexity of the product design, different teams may be required to perform multiple tasks. Before finalising anything, a design engineer may have to make several product sketches to refine the central concept.
4. Prototyping
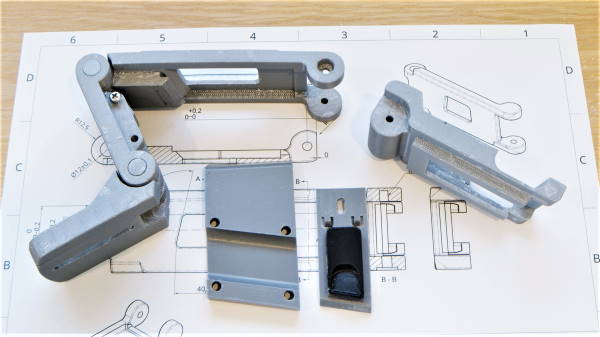
Prototypes are mock-ups that are designed to offer a visual idea of the product before its full-blown manufacturing starts. Prototyping or 3D product modeling is one of the most crucial steps in product design because it lays down the three-dimensional blueprint of the manufacturable product. This step is about creating detailed product specifications in 3D models using computer-aided design (CAD) technology and 3D renderings. Using such technologies, a design engineer gets a skeleton view of the product, allowing the timely identification and rectification of design flaws. After a few iterations, the product is ready for manufacturing.
5. Production of product samples
After the client approves the product prototype, the manufacturing of product samples can start. Pre-production samples help understand whether the product's main essence is viable for execution or not. The ultimate users have to find it attractive. Also, it's essential to set up manufacturing processes and perform a detailed cost analysis. Once the samples are produced and tested, the main production can commence. During this stage, a design engineer is expected to demonstrate ace project management skills and play management roles to streamline processes.
6. Product evaluation and testing
The final step in product design is product testing, which seeks to assure the final users about the quality of the manufactured product. Product evaluation and testing include all quality assurance activities that establish the product's appearance, functionality, and performance. It can be a physical product like a refrigerator, computer system, smartphone, or a digital product like a website or a mobile application. When the activities give a green signal at this stage, the manufactured product is ready for release to the market.
Conclusion

Product design is not a piece of cake for design engineers. A lot of thought and effort goes into it. Each step is defined and laid out to ensure work flows smoothly, and a design engineer has to play a crucial management role. Together with innovative thinking and proper budget management, project management skills and tools can help design engineers overcome most product design challenges.
However, there’s always scope to improve the design process for digital products. The key to designing and successfully launching new products in the market lies in having the fingers on the pulse of the end-users. The more innovative solutions they come across, the greater the chances of the product’s success. No matter how challenging the competition is, out-of-the-box thinking and strategic approach can help a design engineer get the most out of their product design activities.