CAD, or computer-aided design software, has revolutionised the field of product and industrial design since its inception in the early 1960s. Before CAD, designers had to manually sketch their designs on a large swath of paper, laid out on a drafting table. Using lead pencils, T-squares, erasers, and drafting brushes, designers brought to life their ideas in two-dimensional renderings. Needless to say, it was painstaking and time-consuming work. For technical drawings, they are also prone to inaccuracies and mistakes.
When CAD became widely used in a variety of fields, including product design, it paved the way for faster and more efficient product development. This also led to an economic boon for countries that prioritised their design sectors. In New Zealand, the 2013 Value of Design report, conducted by the Minister of Finance Hon. Steven Joyce, revealed that design alone contributed an astounding NZD 10.1 Billion to New Zealand’s GDP (approximately 4.2 per cent). With technologies like CAD boosting product design, (NZ) New Zealand could be a global hub of product innovation in no time at all.
To better learn about CAD and how it works, it’s best to understand what exactly it does and what its role is in modern product design.
What Is CAD?
Computer-aided design (CAD) is a sophisticated technology that utilises computer software to assist in the creation, modification, and optimisation of detailed 2D and 3D models for various products.
In the field of product design, CAD significantly enhances the process by providing a digital canvas where designers can draw and present their ideas. Indeed, CAD has been a transformative tool for designers, engineers, and other professionals involved in developing innovative products and solutions.
Role of CAD in Product Design
CAD goes beyond being a mere drafting tool. It is a powerhouse that propels the entire product design process. Let's delve into the pivotal roles that CAD plays in shaping the trajectory of product development.
1. Provides a Platform for Visualisation and Conceptualisation
In product design, the ability to visualise and conceptualise ideas is incredibly essential. CAD serves as the architect's sketchbook, allowing designers to create intricate 2D and 3D models. This digital platform not only enhances the clarity of design concepts but also fosters a deeper understanding of the product before it takes physical form.
Moreover, CAD enables designers and stakeholders to visualise a product in a variety of ways. For instance, if a client wants to develop a new ergonomic chair, the designer can provide renderings of the same chair in a variety of materials, colours, and perspectives.
2. Facilitates Product Prototyping and Simulation

Prototyping is the litmus test for any product's viability. CAD enables designers to craft virtual prototypes, creating a digital playground for experimentation. By simulating real-world scenarios, potential issues can be identified and addressed early in the design process. As a result, designers can save time and resources when developing physical prototypes.
Take, for example, a design for a standing desk. With CAD, designers can virtually build the desk model, testing its adjustability, stability, and user experience. How will it look retracted? Will computer cables get in the way while extending the table? What should be its maximum height? These are just some of the questions that can be answered during this stage of product development.
3. Enables Product Iteration
Innovation thrives on iteration. CAD empowers designers to swiftly iterate and refine their creations. The ability to make quick and precise modifications to digital models ensures that the final product is a testament to continuous improvement.
Product iteration using CAD involves improving a design through successive cycles. To illustrate, in developing a smartphone, designers can employ CAD to make quick digital modifications to enhance features like camera placement or ergonomics. These iterative changes are efficiently implemented in the CAD model. This allows designers to fine-tune the product's design before proceeding to the manufacturing phase.
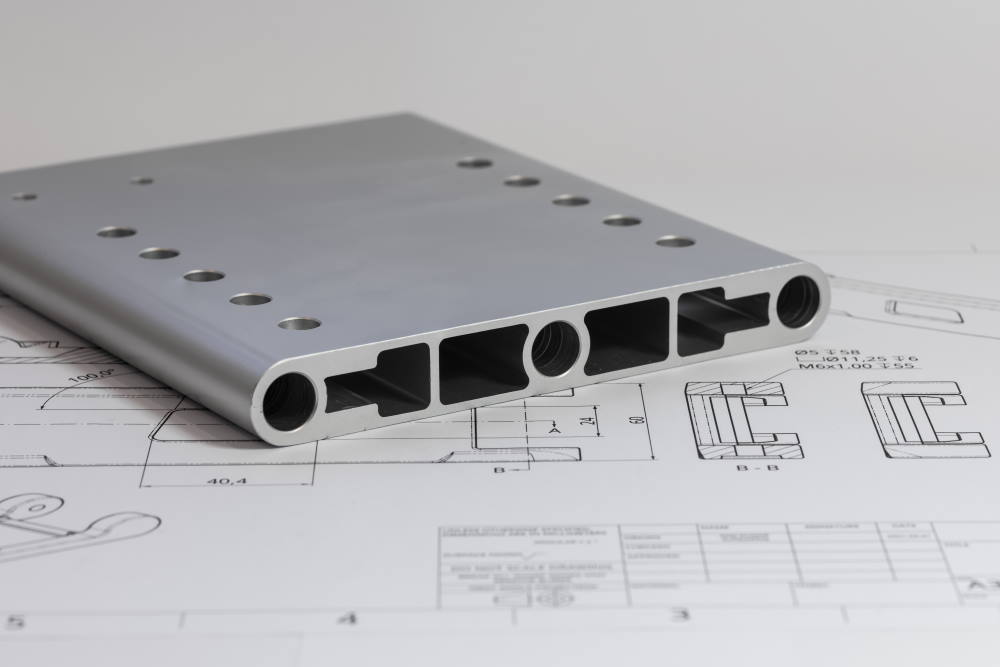
4. Ensures Precision and Accuracy

In product design, precision is one of the most important aspects. For this reason, CAD tools provide an unparalleled level of accuracy in measurements and specifications. It's necessary to ensure that every component fits seamlessly into the overall design.
In conceptualising a complex aerospace component, for example, CAD ensures precision and accuracy by allowing engineers to meticulously define intricate geometries and specifications. To illustrate, the precise measurements of turbine blades and their aerodynamic profiles can be digitally crafted with exacting detail using CAD. This guarantees that each component adheres to the strict tolerances required for optimal performance in the final product.
5. Supports Collaboration
The product designer is not alone in the design and development of new products. Multiple team members, from designers to engineers, can seamlessly work on the same digital model, which fosters efficient communication and coordination. This collaborative environment is vital for the synthesis of diverse expertise.
CAD facilitates collaboration between designers, engineers, and other stakeholders by providing a shared digital platform where everyone can work on the same model simultaneously. For example, in the development of an electric car, designers can use CAD to create the vehicle's exterior, while engineers concurrently refine the internal components.
In doing so, there’s seamless integration and communication between the design and engineering teams throughout the collaborative process. Meanwhile, feedback from stakeholders can also be taken into account during product iterations.
6. Generates Documentation
The devil is in the details, and CAD ensures that no detail is overlooked. Through meticulous documentation, CAD systems pave the way for a smooth transition from the design phase to manufacturing.
CAD can seamlessly generate detailed product design documentation, including precise schematics, assembly instructions, and material specifications. In the development of a new consumer electronics device, for example, this capability ensures that manufacturers possess a comprehensive and accurate blueprint for the production process.
In the ever-evolving landscape of design and innovation, CAD stands as a beacon of transformation. It has not only simplified the way we create and envision products but has also catalysed a revolution in various industries worldwide.
From the intricate artistry of 2D and 3D models to the collaborative symphony of design and engineering teams, CAD has transcended its role as a drafting tool to become the cornerstone of modern product design. As we celebrate the boundless possibilities it brings, let us continue to embrace CAD's power as it continues to push the realm of product design forward.