Industrial design has become a fundamental aspect of the 21st century as it has dramatically influenced the functionality, innovation, and aesthetics of products people use daily. This field, which extends from the smallest household items to large-scale manufacturing, plays a crucial role in determining the usability and appeal of products.
Industrial design has become a fundamental aspect of the 21st century as it has dramatically influenced the functionality, innovation, and aesthetics of products people use daily. This field, which extends from the smallest household items to large-scale manufacturing, plays a crucial role in determining the usability and appeal of products.
Over the years, it has impacted individual user experience as well as broader economic and environmental trends. Industrial design has matured into a global movement where regions like New Zealand have significantly contributed to its gradual rise to modernity and fame. The industrial design NZ market echoes a unique blend of innovation and practicality, where frontrunning companies like Pro-Dev stand out for their skill in transforming creative ideas into tangible, market-ready products.
However, it is essential to note that the evolution of industrial design is a complex narrative driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts, and economic dynamics. From the initial stages of mass production to the sleek designs of today, its development is a testament to the progress of human creativity and industrial capability. Understanding this evolution from a broader vantage point offers valuable insights into the field's past transformations and future potential.
The Genesis of Industrial Design: Early Innovations and Philosophies
The journey of industrial design began in earnest during the Industrial Revolution. This era marked a seismic shift from handcrafted goods to mass production, which altered the entire design landscape. Key figures such as William Morris and Henry Ford emerged, championing philosophies that balanced aesthetics with functionality.
Morris advocated for beauty in everyday objects, while Ford revolutionised production lines and set the foundation for modern industrial design. This period was characterised by rapid technological advancements and a burgeoning appreciation for design that was both practical and pleasing to the eye.
The 20th Century: Functionality Meets Aesthetics
As the 20th century unfolded, industrial design gradually embraced functionality and aesthetics. Walter Gropius founded the Bauhaus movement in early to mid-1900s Germany and became an emblem of this new design ethos. It promoted a fusion of art, craftsmanship, and technology that led to simple yet elegant designs.
The Streamline Moderne movement took this further by introducing aerodynamic forms symbolising speed and efficiency. These movements influenced the shape and functionality of products and reflected a society increasingly focused on progress and modernity.
The Post-War Boom: Consumerism and Mass Production

The post-World War II era ushered in an age of consumerism and mass production that impacted the foundations of industrial design. With a booming economy and technological advancements, there was a surge in consumer demand for a wide array of products. Designers like Raymond Loewy and Charles and Ray Eames rose to prominence, creating affordable, functional, and stylish designs for the masses.
This period saw the proliferation of plastics and other new materials, which allowed for more versatile and innovative designs. The focus of industrial design shifted towards creating products that were both high in quality and accessible to the public.
The Digital Revolution: The Impact of Technology on Design
The advent of the digital revolution in the late 20th century marked a new epoch in industrial design. This era was defined by the rise of computer-aided design (CAD) tools, which completely transformed how designers conceptualised and executed their ideas. These technological advancements enabled more precise and complex designs, pushing the possible boundaries.
The digital age also introduced a level of customisation and flexibility previously unimaginable that allowed designers to experiment with forms, textures, and materials in a virtual space. This period was indeed a turning point that showcased how technology could enhance creativity and efficiency in industrial design.
The Green Wave: Sustainability in Industrial Design
As environmental awareness grew, sustainability became a cornerstone of industrial design philosophy. This shift was not merely about adopting eco-friendly materials but also represented a broader change in thinking about product life cycles, energy consumption, and waste reduction.
Designers began to embrace concepts like cradle-to-cradle design, focusing on creating products that were not only durable and functional but also environmentally responsible. This era saw the peak of techniques that balanced aesthetic appeal with ecological sensitivity, reflecting a growing recognition of our responsibility towards the planet.
The Future is Now: Emerging Trends and Predictions
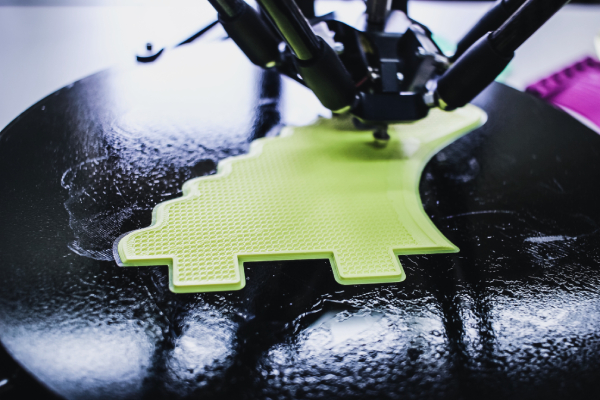

As one peers into the horizon of industrial design, emerging trends paint a picture of a rapidly evolving discipline. The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) in design processes was once a futuristic concept but is now a current reality. AI aids in creating more intuitive and user-responsive products that enable personalisation at an unprecedented scale.
Another significant trend is the rise of 3D printing technology, allowing designers to prototype and produce complex designs easily and quickly. Additionally, the increasing focus on user experience (UX) design signals a transition towards functionally robust, user-friendly, and emotionally resonant products. These developments suggest a future where industrial design is more interactive, customisable, and attuned to the needs and desires of users.
The Social Dimension: Industrial Design and Society
Industrial design does not exist in a vacuum. It influences and is influenced by the societal context in which it operates. Examining the symbiotic relationship between industrial innovation and social trends, cultural shifts, and user behaviours is vital. Design reflects societal values and aspirations, such as the growing emphasis on inclusivity and accessibility in product design. Hence, its significance in today's society cannot be overlooked.
The present concepts of industrial design are marked by a heightened awareness of the social impact of products, from how they are manufactured to how they are used and eventually disposed of. The role of design in shaping everyday life and future societal changes is a testimony to its power and responsibility in crafting a more equitable and sustainable world.
Evolution Through Innovation: The Journey of Industrial Design
The evolution of industrial design throughout the decades is not just about changing styles or technologies; it reflects more profound shifts in how people interact with and think about the objects in the world.
The ongoing narrative of industrial design is rich with potential for breakthroughs and transformative ideas. It offers a lens through which designers, enthusiasts, and consumers can view the evolution of creativity, technology, and human needs. Continuing and improving future developments in industrial design will shape innovative thought, influence design practices, and adapt to the evolving needs of the world.