If you are a fan of spy movies, you will find gadgets not yet invented come to life. Fingerprint scan. Voice activation. Facial recognition. QR Codes.
With these technological breakthroughs, one might think they are living in the realm of science fiction. But many changes in the field of technology allowed us to utilise these advancements.
Facial recognition is one of those technologies whose potential was introduced to us through the big screen. What seemed to be an impossible mission is now used commonly to provide security.
History of Facial Recognition
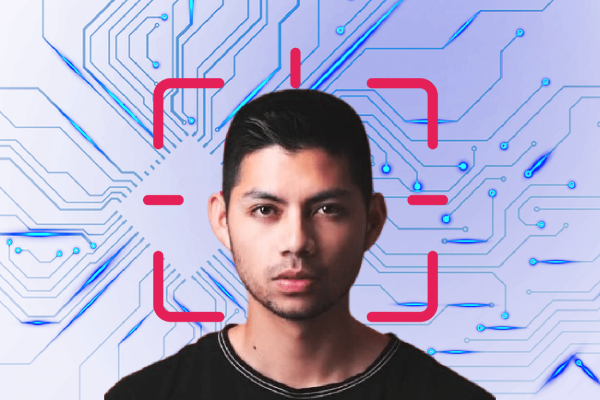 Between 1964 and 1965, using computers for human face recognition began. The distance is automatically computed through various landmarks of the face, and identity is determined. That was the start of a new biometric system - Facial Recognition Technology.
Between 1964 and 1965, using computers for human face recognition began. The distance is automatically computed through various landmarks of the face, and identity is determined. That was the start of a new biometric system - Facial Recognition Technology.
Since the early 2010s, the use of facial recognition technology has developed. 2017 saw a significant breakthrough in the use of facial recognition. Apple launched its new model of the iPhone, and iPhone X integrated the use of facial recognition to unlock with FaceID.
Here are areas that use facial recognition technology:
Security
In addition to catfishing; online scams and identity fraud have increased as we move towards digitalisation.
Scammers find ways to breach security systems and gain unauthorised access to data stored in the cloud. Unauthorised access can lead to the theft of sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, and other personal information.
Multi-factor Authentication is a method of authentication requiring the user to provide multiple verification factors to gain access to sensitive data. There are three types of MFA methods:
Knowledge
You have personal knowledge of these things, e.g. passwords, pins, and security questions.
Possession
You own things, such as your credit card or smartphone.
Inherence
These are things that are unique to you, such as biometrics. You can qualify the following under inherence: fingerprints or voice recognition. It is also where we can categorise facial recognition.
The use of facial recognition can streamline processes, allowing access to applications and other online services.
 Establishments/Commercial Spaces
Establishments/Commercial Spaces
Many establishments are also moving towards digitalisation in securing entry into their premises. For example, facial recognition biometrics is used to determine a person's identity and allow them entry if deemed safe.
Apple is also not the only brand that integrated facial recognition into its security upgrade. Samsung and other big phone brands have also incorporated the same. This is done majorly for the convenience of unlocking your phone without entering a password. Smart doorbells now allow the homeowner to view the person requesting entry to their homes. Office space managers also encourage using mobile apps to reserve space or make appointments. Even public transportation, schools, and other areas use facial recognition technology.
Financial Services
Most banking institutions also have digital platforms to conduct faster and hassle-free transactions. In addition, banks are now moving towards using facial recognition to verify the user's identity.
Customers are asked to provide a document that displays their photos. The application will then require them to take a selfie and establish the live identity of the user.
'How do they determine whether the person in the document and the person in the self-captured photo are the same?' You may ask.
The technology will conduct a likeness check where the facial landmarks will play an important role. They calculate eye placement, distances between each other and the chin, and other pertinent details.
If you have experience applying to any of these online platforms, you know that they sometimes ask you to 'nod' or 'blink'. They refer to this as the "liveness" check to determine if the selfie is from a live person and not doctored.
Healthcare
Expedited and secured access to medical information is a focus of development in the health field, even more so after the pandemic,since access to medical records has become increasingly valuable.
This information is confidential and has been the subject of cybercrimes involving identity theft. The patients and care providers cannot afford the risk of compromised passwords. Hence, biometric scanning makes it convenient to access any sensitive information.
In the delivery of care front, using biometrics provides faster access to medical records and a patient's history. As a result, medical professionals can immediately administer treatment based on the patient's overall health. And make care decisions better, improving the quality of care and helping save lives.
Law enforcement
There is a reported increase in the use of facial recognition technology among law enforcement agencies. Mugshots from arrestees are collected by law enforcement officers and compared with face recognition databases.
Once the photo of an arrestee is taken, it will be added to databases for scanning whenever law enforcement agents conduct another criminal search.
Mobile face recognition also makes it convenient for law enforcement officers. For example, with handheld devices, photos of a driver or a pedestrian in the field may be taken and immediately compared with one from face recognition databases to attempt an identification.
Some video surveillance systems are linked to biometrics data and criminal databases. These systems are installed with face recognition allowing agencies to scan footage taken by these cameras in real time and determine the identity of a known criminal or persons of interest in a heavily crowded place.
Airport border and Control
Airports around the world are now integrating the use of facial recognition in their operations.
The use of facial recognition reduces waiting time for travelers and allows the improvement of airport security. In addition, it is convenient for travelers to skip long lines and walk through an automated ePassport control system to reach the gate faster.
It is expected that airports and border crossings will use facial recognition to enhance security at large-scale events such as general assemblies or the Olympics.
Social Media and Applications
Social media companies and app developers have heavily utilised facial recognition technology. Facebook used facial recognition to help identify faces featured in photos of Facebook users.
Several other applications also use facial recognition. And growth may be seen exponentially through social apps that facilitate the creation of avatars and stickers based on the person’s facial features and appearance.
Some of these applications and social media sites also use facial recognition for security.
Retail and Advertising
Commercial establishments are also seizing the opportunity in the advertising field. A start-up company in the Philippines, AdMov, installed tablets in taxis with facial recognition technology. The software will select the kind of advertisement to display based on your mood as determined by the system.
AdMov is also taking it a step further by tracking eyeball movement and detecting if the passenger is disengaged, and it changes the programme and strategy accordingly.
Marketers are utilising facial recognition to improve consumer experiences. Some companies use facial recognition to gauge people’s reactions and better understand the audience's preferences.
Although there are some concerns about the use of facial recognition technology, implementation has been slow because of privacy concerns from most people.

Conclusion
The technology behind facial recognition is becoming increasingly sophisticated. It offers exciting possibilities for safeguarding sensitive information, better estimating who will click on specific ads or purchase certain products, and even identifying individuals who may be dangerous or prone to criminal activity.
Facial recognition is a complex and challenging technology, but it's a technology that's here to stay. Organisations worldwide have already implemented facial recognition in various security systems, and we can expect to see these implementations become more prevalent. It's a new way of thinking about security.